Do pi bonds affect molecular geometry?
Table of Contents
- Do pi bonds affect molecular geometry?
- What factors affect bond angles?
- What is causing the angles to skew?
- Are pi bonds rotatable?
- What does a pi bond look like?
- Is a triple bond sigma or pi?
- What two factors can alter ideal bond angles?
- Do double bonds decrease bond angles?
- How does size affect bond angle?
- How are pi bonds different from P bonds?
- How does π bond affect the geometry of a molecule?
- Which is the nodal plane for the pi bond?
- Where do pi and sigma bonds occur in a molecule?
Do pi bonds affect molecular geometry?
As such, π bonds do not alter the basic idealized geometry of a molecule as dictated by σ bonding, although in practice, because they do actually introduce additional electron density and require closer orbital overlap, bond multiplicity affects bond length and bond angles (as does, for that matter, the size of the ...
What factors affect bond angles?
1 Answer
- Hybridization: Bond angle depends on the state of hybridization of the central atom. ...
- Lone pair repulsion: Bond angle is affected by the presence of lone pair of electrons at the central atom. ...
- Electronegativity: If the electronegativity of the central atom decreases, bond angle decreases.
What is causing the angles to skew?
The extra pairs of electrons on the central atom are called 'lone-pairs'. Bond angles will deviate from their ideal values according to the rule that lone pairs repel other electrons more strongly than bonding pairs. ... Being closer to the central atom causes lone-pairs take up more of the available 'bonding space'.
Are pi bonds rotatable?
No, pi bonds cannot rotate. When a pi bond is formed, all the pieces of a molecule are locked in place. This is one reason cis- and trans- isomers are formed.
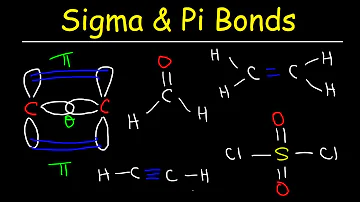
What does a pi bond look like?
The pi bond is the "second" bond of the double bonds between the carbon atoms, and is shown as an elongated green lobe that extends both above and below the plane of the molecule. ... Both the py and the pz orbitals on each carbon atom form pi bonds between each other.
Is a triple bond sigma or pi?
In general, single bonds between atoms are always sigma bonds. Double bonds are comprised of one sigma and one pi bond. Triple bonds are comprised of one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
What two factors can alter ideal bond angles?
Many factors lead to variations from the ideal bond angles of a molecular shape. Size of the atoms involved, presence of lone pairs, multiple bonds, large groups attached to the central atom, and the environment that the molecule is found in are all common factors to take into consideration.
Do double bonds decrease bond angles?
However, the double bond seems to act much like a nonbonding pair of electrons, reducing the ClCCl bond angle from 120° to 111°. In general, electron domains for multiple bonds exert a greater repulsive force on adjacent electron domains than do single bonds.
How does size affect bond angle?
As the size of the central atom increases, the bond angles decrease; thus, we observe a negative relationship between size of the central atom and the bond angle in these molecules. ... As the central atom increases in size, the bond lengths also increase and the pendant atoms are farther from each other in space.
How are pi bonds different from P bonds?
It is important to note that the head-to-head overlapping of two p orbitals gives a sigma bond whereas the lateral overlap of these orbitals leads to the formation of pi bonds. Pi bonds are formed by the sidewise positive (same phase) overlap of atomic orbitals along a direction perpendicular to the internuclear axis.
How does π bond affect the geometry of a molecule?
As such, π bonds do not alter the basic idealized geometry of a molecule as dictated by σ bonding, although in practice, because they do actually introduce additional electron density and require closer orbital overlap, bond multiplicity affects bond length and bond angles (as does, for that matter, the size of the atoms involved).
Which is the nodal plane for the pi bond?
The two orbitals which are bonded share the same nodal plane at which the electron density is zero. This plane passes through the nuclei of the two bonded atoms and is also the nodal plane for the molecular orbital corresponding to the pi bond.
Where do pi and sigma bonds occur in a molecule?
(CC BY-NC; CK-12) The sp hybrid orbitals form a sigma bond between each other as well as sigma bonds to the hydrogen atoms. Both the py and the pz orbitals on each carbon atom form pi bonds between each other. As with ethene, these side-to-side overlaps are above and below the plane of the molecule.

 Main Topics
Main Topics


