What is ALD medical term?
What is ALD medical term?
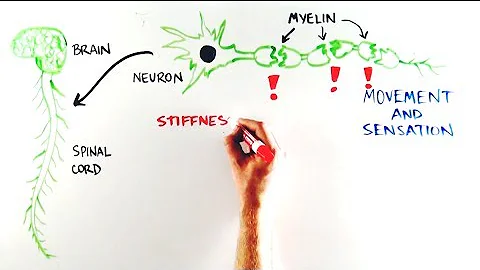
What is ALD? Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a genetic condition that damages the membrane (myelin sheath) that covers nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. Myelin acts as insulation around the nerve fibers.
How do you test for ALD?
When a clinician suspects ALD, they will perform two tests — a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to determine whether there is damage to the brain tissue and a blood test to measure the concentration of very long chain fatty acids, which are elevated in males with ALD.
What happens if you have ALD?
Gradually, as the disease spreads throughout the brain, their symptoms grow worse. Some symptoms could include blindness, deafness, seizures, loss of muscle control and progressive dementia. This form of ALD is characterized by an inflammatory process that destroys the myelin.
How is a prenatal diagnosis of ALD done?
Prenatal diagnosis is the diagnosis of a genetic disease before a baby is born. It entails collecting a DNA sample from the fetus and analyzing it with genetic testing. In the case of ALD, the sample is used to look for mutations in the ABCD1 gene.
How is ALD related to the X chromosome?
ALD is an X-linked recessive condition caused by a mutation in the ABCD1 gene on the X chromosome. Because a female has two X chromosomes, if she inherits the faulty gene, then she still has another X chromosome to offset the mutation. However, because males only have one X chromosome, the gene abnormality causes the disease.
What are the chances of having a child with ALD?
With each pregnancy, female ALD carriers have a 25 percent (1 in 4) chance of having a carrier daughter and a 25 (1 in 4) percent chance of having a son affected with the disease. What are the symptoms of ALD? Boys with cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy usually begin showing symptoms between the ages of 4 and 10.
Which is the most common form of ALD?
The most common type of ALD is X-linked ALD, which is caused by a genetic defect on the X chromosome. X-linked ALD affects males more severely than females, who carry the disease. Forms of X-linked ALD include: Childhood-onset ALD. This form of X-linked ALD usually occurs between ages 4 and 10.

 Main Topics
Main Topics


