What does dehydration synthesis create?
Table of Contents
- What does dehydration synthesis create?
- Does dehydration synthesis remove or add water?
- How much water is removed in dehydration synthesis?
- Does dehydration reaction use water?
- What is an example of dehydration reaction?
- Why is the process of dehydration called synthesis?
- Why is dehydration a type of condensation reaction?
- What happens to three water molecules during dehydration?
- What is the difference between hydrolysis and dehydration?
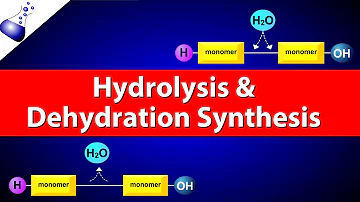
What does dehydration synthesis create?
Dehydration synthesis is the creation of larger molecules from smaller monomers where a water molecule is released. This can be used in the creation of synthetic polymers such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), or the creation of large biological molecules such as carbohydrate polymers and triglycerides.
Does dehydration synthesis remove or add water?
Dehydration synthesis is the process of joining two molecules, or compounds, together following the removal of water. When you see the word dehydration, the first thing that may come to mind is 'losing water' or 'lacking water. ' This is a perfect way to remember what occurs during a dehydration reaction.
How much water is removed in dehydration synthesis?
Many reactions involving dehydration synthesis are associated with the formation of biological polymers where the addition of each monomer is accompanied by the elimination of one molecule of water.
Does dehydration reaction use water?
In chemistry, a dehydration reaction (a.k.a. condensation reaction), also known as Zimmer's Hydrogenesis, is a conversion that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes, the reverse of a hydration reaction.
What is an example of dehydration reaction?
Formation of maltose is an example of a dehydration synthesis reaction. Two alpha-glucose units form a glycosidic linkage with elimination of water molecule to form one maltose molecule.
Why is the process of dehydration called synthesis?
The process of combination of two molecules with the elimination of water molecule is called dehydration synthesis.” This is because the term dehydration is used for ‘losing water’ and synthesis represents the formation of the new substance, therefore, dehydration synthesis is the elimination of water with the formation of new compounds.
Why is dehydration a type of condensation reaction?
Here in dehydration synthesis reactions, since water molecule eliminates during the reaction, therefore, they are also a type of condensation reactions. This is because during the condensation reaction two molecules condense to form a large molecule with loss of water molecule. What is Substitution Reaction?
What happens to three water molecules during dehydration?
The removal of three water molecules in the process of forming a triglyceride further increases the energy density of the molecule. In this image, R1, R2 and R3 refer to long chain hydrocarbons, each of which is attached to a carboxylic acid functional group.
What is the difference between hydrolysis and dehydration?
In Chemistry, Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction with water, in which a macromolecule is separated into smaller molecules. On the other hand, in Biology, this process involves water to split polymers into monomers.

 Main Topics
Main Topics


